The Arctic ecosystem is a complex and delicately balanced web of life, in the food chain, where consumers, producers, and the changing climate all play pivotal roles in shaping its destiny. Understanding the unique challenges faced by creatures like the Arctic fox within this ecosystem is not only a scientific endeavor but a call to action to preserve the irreplaceable wonders of the frozen North for generations to come. This article will discuss the fascinating Arctic Fox in the Food Chain and Ecosystem. Keep reading.
Interesting Facts about the Arctic Fox Food Chain
The Arctic fox, like all other creatures inhabiting the intricate web of life, plays an indispensable role within its respective ecosystem. This seemingly unassuming member of the animal kingdom, cloaked in its pristine white fur, holds a pivotal position in the natural food chain. It’s a creature that exemplifies the balance and interdependence that underpins the intricate dance of life in the frigid expanses of the Arctic. Here we go with some of the interesting facts about Arctic Fox Food Chain:
1. A Secondary Consumer in the Food Chain
Within this carefully orchestrated symphony of survival, the Arctic fox assumes the role of a secondary consumer. It perches comfortably in the middle tiers of the food chain, relying on the activities of those species dwelling a rung below it. These primary consumers, such as caribou and rabbits, subsist on the sparse vegetation that manages to eke out an existence in the harsh Arctic environment. They, in turn, serve as the vital sustenance for the Arctic fox.
2. Completing the Food Chain
To understand the Arctic fox’s place in the grand scheme of Arctic life, it is essential to recognize that ecosystems are multifaceted, intricate systems. The Arctic food chain extends further, encompassing apex predators at its summit. These formidable creatures, including polar bears, wolves, and hawks, stand as the tertiary predators, keeping a watchful eye on the living Arctic foxes, as well as the primary consumers dwelling beneath them.
The Arctic fox’s presence in the Arctic ecosystem thus represents a linchpin, bridging the gap between primary consumers and top-tier predators. It plays a role not just as a consumer but as a conduit for the transfer of energy and nutrients between these different strata of the food chain. In essence, the Arctic fox symbolizes the delicate equilibrium that characterizes life in one of the world’s harshest and most unforgiving environments, where survival is a testament to the intricate dance of nature.
3. Cyclic Lemming Populations and Their Impact
Cyclic lemming populations, an essential component of the Arctic ecosystem, play a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. These small, furry rodents serve as the primary prey for the resourceful Arctic foxes. A fascinating phenomenon unfolds as the lemming populations oscillate cyclically. This lemming cycle, in turn, triggers a corresponding cycle in the Arctic fox population, where these clever canines adapt their numbers to the abundance of their primary food source.
However, the intricacies of this interconnected web of life do not end there. The fluctuations in the Arctic fox population, driven by the lemming cycle, have a ripple effect on the demographics of Arctic geese. These geese, being an alternate source of sustenance for the foxes, experience their demographic cycles in response to the changing fox numbers. It’s a complex dance of survival and adaptation, where every species must keep a delicate equilibrium to ensure a continuous supply of food, thereby highlighting the intricacies of nature’s grand design.
4. The Arctic Food Chain Hierarchy Unveiled
Understanding the Arctic’s intricate food chain hierarchy is vital to comprehend the web of life in this harsh and unforgiving environment. At the apex of this frigid ecosystem stands the polar bear, a majestic and formidable creature known as the Tertiary Consumer. Just below this formidable apex predator is the Arctic fox, a cunning hunter, and the Secondary Consumer. Further down the chain lies the humble lemming, the Primary Consumer, whose existence forms the foundation of this intricate web of life.
The Producers in this ecological narrative are the lichens, hardy organisms capable of surviving in the harshest Arctic conditions, providing a vital source of sustenance for the primary consumers. Lastly, the decomposers, represented by Arctic moss, play a critical role in recycling nutrients and ensuring the ecosystem’s health. This hierarchy beautifully illustrates the interdependence and complexity of Arctic life.
5. The Vital Role of Lichen in Arctic Ecosystems
Lichens, often overshadowed by their larger and more charismatic counterparts, are the unsung heroes of the Arctic ecosystem. These remarkable organisms serve as the lifeblood of the region, contributing a staggering 100% of the vitality that sustains the intricate web of Arctic life. What makes lichens truly remarkable is their ability to thrive throughout the year, defying the extreme conditions of the Arctic.
Their constant growth ensures a consistent food source for the next link in the food chain. Lemmings, the primary consumers, derive 10% of their vitality from these hardy lichens, while Arctic foxes, the secondary consumers, receive a mere 1%. Even the mighty polar bear, the tertiary consumer, only gets a fraction, a mere 0.01%, of its vitality from these unassuming but vital lichen communities. The cycle of life in the Arctic depends on this delicate allocation of energy and resources.
6. The Arctic Fox as the Secondary Consumer
In the Arctic food chain, the Arctic fox assumes the role of the secondary consumer, positioned just below the dominant polar bear. This fox, with its elegant and efficient hunting strategies, forms a critical link in the ecosystem, serving as a bridge between the primary consumers, such as lemmings and geese, and the top-tier predator, the polar bear. Through its adaptability and resourcefulness, the Arctic fox keeps the intricate balance of nature intact, ensuring the survival of both its species and those it preys upon.
7. Predators of the Arctic Fox
While the Arctic fox may occupy a significant position in the Arctic food chain, it is not without its own set of challenges. These resilient creatures face threats from various predators, each playing a unique role in the ecosystem. Pink foxes, wolves, wolverines, and polar bears all pose a formidable threat to the Arctic fox population. Even the youngest members of the fox family, the fox pups, are not safe from predation. Birds of prey, including snowy owls, great hawks, and jaegers, complete the intricate picture of the Arctic food chain. The harsh reality of life in the Arctic underscores the constant struggle for survival, with each species playing a distinct role in the grand scheme of things.
8. Arctic Fox’s Dietary Preferences
The Arctic fox, renowned for its remarkable adaptability, derives its energy and sustenance from a variety of sources. One of its primary food sources is the arctic hare, a fellow inhabitant of this frigid landscape. With its keen hunting instincts, the Arctic fox preys upon the arctic hare, ensuring its survival in this challenging environment. This predator-prey relationship exemplifies the intricate web of life in the Arctic, where each species contributes to the ecosystem’s intricate balance.
9. The Arctic Food Chain in Action
In the grand narrative of the Arctic food chain, energy flows seamlessly from one level to another, supporting the survival of each species. The journey begins with the life-giving energy of the sun, which nourishes the resilient grasses and sedges that thrive in the harsh Arctic conditions. These plants, in turn, provide sustenance for the arctic hare, a primary consumer. The agile and resourceful Arctic fox preys upon the Arctic hare, acting as the secondary consumer in this chain.
Finally, at the peak of this frozen hierarchy stands the Arctic wolf, representing the ultimate predator in this unforgiving ecosystem. This intricate sequence of life exemplifies the remarkable complexity and interdependence that characterizes the Arctic food chain, ensuring the survival of all its inhabitants.
10. Consumers in the Arctic Ecosystem
In the intricate web of life within the Arctic ecosystem, consumers play a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. Among these consumers, the majestic Arctic wolf stands out as a remarkable apex predator, a creature that draws its vitality from the very essence of the Arctic wilderness. These awe-inspiring predators depend on the Arctic fox, a vital component of their diet. In the harsh Arctic environment, the wolf is a prime example of nature’s efficiency, utilizing the energy and sustenance provided by the Arctic fox to fuel its existence.
11. Producers Nurturing Arctic Life
Conversely, while the Arctic wolf symbolizes the consumers within this ecosystem, the producers, such as the resilient grass and sedge, are the unsung heroes that harness the sun’s energy to facilitate growth and nourishment in this frigid environment. These resilient plants serve as the primary source of sustenance for the Arctic herbivores, which, in turn, become prey for the Arctic’s top predators. It is through this intricate interplay between producers and consumers that the Arctic’s unique ecosystem maintains its vitality and diversity.
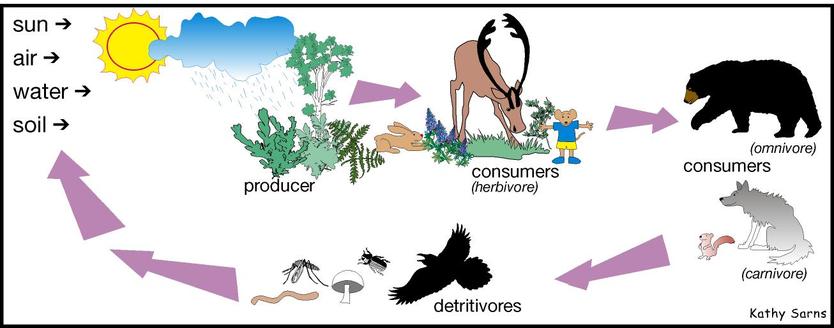
12. Global Warming’s Implications on the Arctic Fox
The looming specter of global warming casts a shadow over the Arctic, with its myriad consequences touching every facet of life in this region. One of the most vulnerable species facing the brunt of these changes is the Arctic fox, the sole endemic terrestrial predatory mammal in the Arctic. The implications of rising temperatures are profound and far-reaching, raising concerns about the future of this remarkable creature.
13. Coastal vs. Inland Arctic Fox Populations
As we delve deeper into the world of the Arctic fox, it becomes evident that there is a significant disparity between coastal and inland populations. Coastal foxes often rely on the marine environment and its associated resources, making them adaptable to a variety of circumstances. In contrast, inland foxes face a more challenging existence, as they primarily depend on the peak abundance of lemming prey to sustain viable populations. The intricate relationship between these foxes and their prey becomes even more pronounced in the face of global warming, as they are profoundly affected by the changing Arctic landscape.
14. Warming Winters and the Lemming Predicament
One pressing concern is the shift in temperature patterns, particularly the milder winters that have become increasingly prevalent due to global warming. These warmer winters can lead to a perplexing phenomenon – the decline in lemming populations, which is a primary food source for inland Arctic foxes. The shortage of lemmings, caused by a disrupted ecosystem, poses a serious challenge to the survival of these foxes. As the intricate web of life in the Arctic unravels, these short-term consequences hold profound implications for the long-term health of the Arctic ecosystem.
15. A Glimpse into the Tundra’s Food Chain
In the frozen expanse of the Tundra, a delicate and intricate web of life unfolds, showcasing the relentless struggle for survival in one of Earth’s harshest environments. This glimpse into the food chain in the Tundra offers a window into the remarkable flow of energy that sustains life in this unforgiving realm. It’s essential to remember that this food chain is just a single thread in the intricate tapestry of a more comprehensive food web, which encompasses not only producers but also a diverse array of consumers, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
16. Producers Nurturing the Chilled Earth
At the very foundation of this ecosystem lie the producers, the life-giving entities that defy the harshness of the Tundra’s climate. These stalwart organisms include grasses, lichens, and caribou moss. They are the true pioneers, summoning life from the frozen earth with their resilience. Through photosynthesis, they convert meager sunlight into sustenance, providing the initial sustenance that fuels this intricate dance of survival.
17. The Herbivores’ Struggle for Sustenance
In the relentless battle for survival, herbivores come into play, seeking nourishment from the resilient producers. The musk ox, a symbol of strength in the Tundra, grazes upon these grasses, alongside the nimble arctic hare and the unassuming lemmings, whose sheer numbers attest to their vital role in this frozen ecosystem. These herbivores navigate the icy terrain, enduring bone-chilling temperatures and the constant threat of predation in their quest for sustenance.
18. Carnivores: The Tenacious Predators
The Tundra’s carnivores are exemplars of tenacity and adaptability. Among them, the cunning arctic foxes and the massive brown bears rise to prominence. Their existence depends on the success of the herbivores, as they skillfully stalk and capture their prey. The chase, fraught with challenges, unfolds on the icy plains, where the balance of life teeters on a knife’s edge. At the summit of the carnivore hierarchy are the majestic snowy owls, the elusive arctic wolves, and the apex predators, polar bears, all of whom subsist on a diet of other carnivores.
19. Apex of the Tundra’s Food Pyramid
And atop this intricate pyramid of life stands man, the ultimate predator. In a landscape where survival is an arduous battle, humans have adapted to exploit the resources of the Tundra. They hunt the arctic wolves and bears, not only for sustenance but also for their fur, a testament to human resourcefulness and adaptation. In doing so, man not only becomes a part of this intricate food chain but also disrupts the fragile balance of this ecosystem, introducing complexities that ripple through the entire web of life.
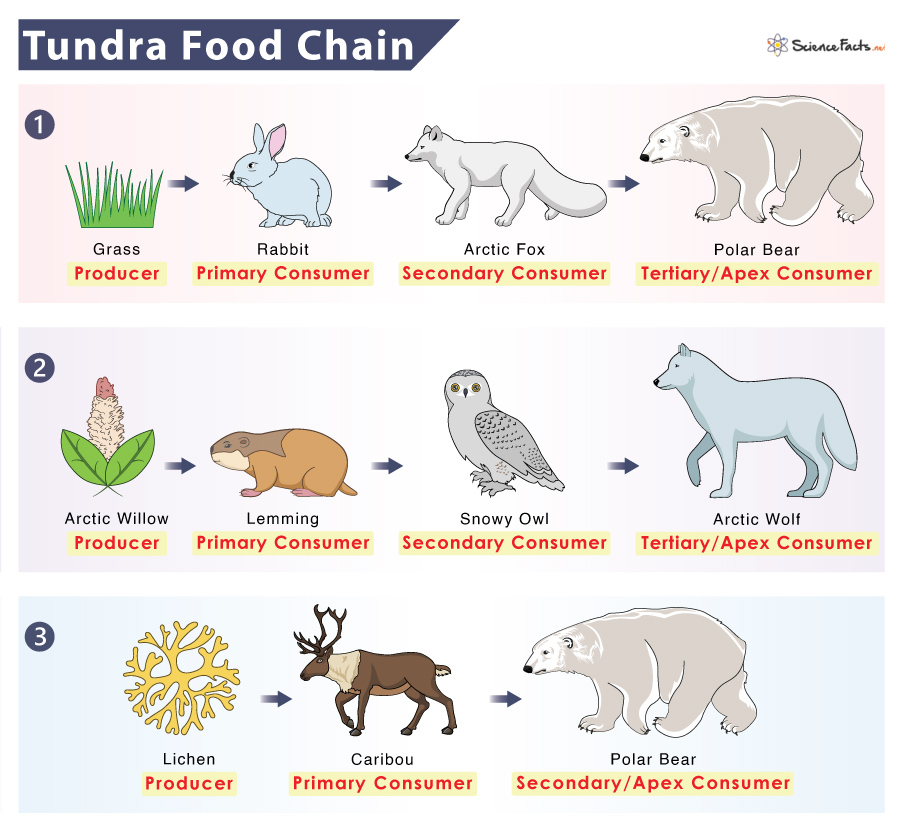
20. Visualizing the Tundra’s Food Chain
For a more visual understanding of the Tundra’s food chain, refer to the diagram below. It provides a hierarchical representation of the relationships within this ecosystem, from the foundation of producers to the apex predators, offering a captivating snapshot of the interconnectedness and interdependence that govern life in the unforgiving Tundra.
21. Omnivore: The Enigmatic Snowy Owl
The enigmatic snowy owl, a striking bird of the Arctic, possesses a unique set of characteristics that distinguish it from its avian counterparts. With piercing golden eyes that glisten in the harsh polar light, these majestic creatures are equipped with claws lined with feathers, adding to their distinctive charm. It is under the cover of the Arctic night that they embark on their hunting expeditions, preferring the cloak of darkness to the blinding daylight.
Snowy owls are predominantly found in the vast, treeless expanses of the Arctic tundra. Their nomadic nature leads them on a relentless quest for sustenance. With open landscapes devoid of trees, these birds must rely on their keen sense of sight and patience to secure their nourishment. Their primary hunting strategy involves perching on the barren ground, poised to seize delectable prey such as Arctic foxes, lemmings, and an assortment of other avian and aquatic species. The snowy owl’s weaponry includes sharp, talon-like claws and eyesight sharp enough to discern prey from considerable distances. These attributes make them masterful predators in the unforgiving Arctic terrain.
22. Carnivore: The Resilient Arctic Fox
In the frosty realm of the Arctic, the Arctic fox, a remarkable mammal, has evolved to thrive in the most adverse conditions. With its endearing short ears and a plush, white fur coat, it maintains not only a level of insulation essential for survival but also a means of camouflage amidst the snow and ice. This striking adaptation allows the Arctic fox to blend seamlessly with its surroundings, rendering it nearly invisible to both prey and predators alike.
While the ability to blend into the Arctic landscape is a formidable defense, it is not an infallible one. Occasionally, the Arctic fox falls victim to formidable adversaries such as bears and owls, who are keen to exploit any weakness. In response, the Arctic fox has developed an additional set of skills. It constructs intricate tunnels and burrows within the snow, creating shelter from the harsh elements and moving silently to stalk its prey.
23. Herbivore: The Tenacious Lemming
Lemmings, diminutive creatures resembling tiny mice, are remarkable herbivores of the Arctic ecosystem. Their very survival hinges on their remarkable adaptability, particularly their ability to camouflage themselves adeptly to evade potential predators. With minuscule claws ideal for digging tunnels through the snow, lemmings ingeniously craft burrows for protection against the relentless threats that permeate the Arctic food chain.
In the winter, lemmings don a white fur coat, blending harmoniously with the snow-covered terrain, while in the summer, their fur transforms, adopting a browner hue to match their evolving environment. Despite their crafty survival strategies, many lemmings still fall prey to the relentless Arctic bear, a constant threat to their existence. The delicate balance between the living and the fallen is essential for the lemming population’s persistence and, consequently, the Arctic ecosystem’s equilibrium. Pet accessories on Amazon
24. Producer: The Prolific Lichen
Lichens, often overlooked as unassuming organisms, are prolific producers with an essential role in the Arctic’s delicate ecosystem. These humble plants are a symbiotic union of fungus and green algae, and their ability to consume carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is nothing short of remarkable. They proliferate across the frigid expanses of the Arctic, adorning rocky coasts, crowning mountain summits, and carpeting icy regions.
Lichens exhibit their astonishing adaptability by thriving in a diverse range of environments, from tropical forests to barren rocks and soils. Their ubiquitous presence in the Arctic ecosystem serves as a critical source of sustenance for various herbivores and, by extension, carnivores. In a region where food sources are scarce, the abundance of lichens plays a pivotal role in sustaining life, making them an unsung hero in the intricate web of Arctic survival.
Other Recommended Articles
- European Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Size | Pet | Baby
- Campbell’s Dwarf Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Colors | Size
- Winter White Dwarf Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Color | Eyes | Pet
- Mongolian Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Dwarf | Range | Diet
- Turkish Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Habitat | Diet | Pet
- Romanian Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Diet | Range | Baby
- Syrian Hamster – Profile | Facts | Traits | Size | Color | Cute | Poop
- 19 Different Types of Hedgehogs – Profile | Facts | Traits | Pet
- Four-Toed Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Size | Cute | Baby
- European Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Size | Pet | Habitat
- Woodland Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Baby | Diet | Range
- Northern White-Breasted Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits
- Amur Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Distribution | Diet
- Indian Hedgehog – Animal | Profile | Facts | Traits | Protein | Habitat
- Indian long-Eared Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Diet | Habitat
- Daurian Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Diet | Distribution
- African Pygmy Hedgehog – Pet | Profile | Facts | Traits | Habitat | Color
- North African Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Lifespan | Habitat
- Somali Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Diet | Distribution
- Desert Hedgehog – Profile | Facts | Traits | Habitat | Cute | Pet
